Книга: Introduction to Microprocessors and Microcontrollers
Two types of RAM
Two types of RAM
Ram chips can be designed in two different forms which we call static RAM (SRAM) and dynamic RAM (DRAM), as seen in Figure 6.16.
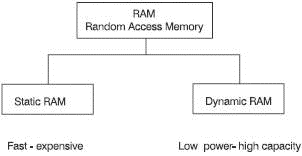
Figure 6.16 The two types of RAM
Static RAM
These are constructed of flip-flops. The problem with the flip-flop is that it draws current all the time. Therefore, it tends to get rather warm and, on a single chip, the components cannot be packed together very tightly. The benefit is that they are very fast and are used where speed of access is important. Static RAM is often called SRAM.
Dynamic RAM
These store the information in capacitors, which are small components that store an electrical charge in the form of static electricity. They are called ‘dynamic’ owing to one of its drawbacks. In use, the electricity stored in each capacitor leaks away because of the imperfect insulation. So, after a little while the charge has to be replaced otherwise the DRAM will be empty and all the stored information will be lost. This replacing is called ‘refreshing’ and has to be performed at intervals of about 2 ms by a DRAM control circuit. To prevent any interference with the operation of the microprocessor system, the refreshing is done in the background whenever the DRAM is not being used.
Once the static charge is stored, no further current is required (except for refreshing), therefore less heat is being generated internally and we can pack more memory into a given space. We say it has a high packing density.
- A flip-flop or bistable
- A register
- Shift registers
- Rotate registers
- Memories
- RAM
- Accessing memory
- Two types of RAM
- Memory organization
- Three types of ROM
- Pin layout of an EPROM
- Pin layout of a SRAM
- Pin layout of a DRAM
- Some more memories that don’t fit into the general pattern
- Memory maps
- Quiz time 6
- 9.2 Remote Frame
- 9.6 Types of Errors
- Other Types of Hardware
- Summary of ipfwadm Arguments
- ICMP datagram types
- Accounting of ICMP Datagrams
- Network Devices Supporting IPX
- 1.9.2 Types and interfaces
- Types of Subprojects
- Appendix C. ICMP types
- Parameter problem
- 2. How to Apply These Terms to Your New Programs




