Книга: Introduction to Microprocessors and Microcontrollers
Using just two digits
Using just two digits
If we reduce the number of digits then a wider voltage range can be used for each value and the errors due to noise are likely to occur less often.
We have chosen to use only two digits, 0 and 1, to provide the maximum degree of reliability. A further improvement is to provide a safety zone between each voltage. Instead of taking our supply voltage of 3.3 V and simply using the lower half to represent the digit 0 and the top half for 1, we allocate only the lower third to 0 and the upper third to 1 as shown in Figure 2.9. This means that the noise level will have to be at least 1.1 V (one-third of 3.3 V) to push a level 0 digit up to the minimum value for a level 1.
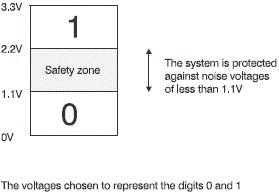
Figure 2.9 A better choice of voltages
Оглавление статьи/книги
- The noise problem
- A complete cure for electrical noise
- Thermal noise
- Partition noise
- How much noise can we put up with?
- Using just two digits
- How do we count?
- The basic basis of bases
- Counting with only two figures
- Confusion and the cure
- Converting denary to binary
- Converting binary to denary
- Bits, bytes and other things
- Quiz time 2
Похожие страницы
- Caveats using NAT
- Using Double Quotes to Resolve Variables in Strings with Embedded Spaces
- Data Binding Using the GridView Control
- Using the kill Command to Control Processes
- It’s All The Same, Just Different
- Part Two - Regulation By Code
- CHAPTER 14 Networking
- Installing Using a Network
- Network Configuration
- Configuring Wireless Networks
- Using X
- Using a Display Manager




