Книга: Mastering VMware® Infrastructure3
Virtual Switch Port Load Balancing
Virtual Switch Port Load Balancing
The vSwitch port-based load-balancing policy that is used by default uses an algorithm that ties each virtual switch port to a specific uplink associated with the vSwitch. The algorithm will maintain an equal number of port-to-uplink assignments across all uplinks to achieve load balancing. As shown in Figure 3.24, this policy setting ensures that traffic from a specific virtual network adapter connected to a virtual switch port will consistently use the same physical network adapter. In the event that one of the uplinks fails, the traffic from the failed uplink will failover to another physical network adapter.
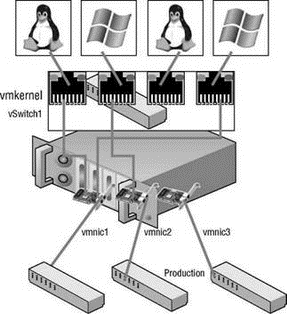
Figure 3.24 The vSwitch port-based load-balancing policy assigns each virtual switch port to a specific uplink. Failover to another uplink occurs when one of the physical network adapters experiences failure.
You can see how this policy does not provide load balancing of the amount of traffic because each virtual machine can access only one physical network adapter at any given time. Since the port to which a virtual machine is connected does not change, each virtual machine is tied to a physical network adapter until failover occurs. Looking at Figure 3.24, imagine that the Linux virtual machine and the Windows virtual machine on the far left and far right are the two most network-intensive virtual machines. In this case, the vSwitch port-based policy has assigned both of the ports used by these virtual machines to the same physical network adapter. Meanwhile, the Linux and Windows virtual machines in the middle, which both might be processing very little traffic, are connected to ports assigned to individual physical network adapters.
The physical switch passing the traffic learns the port association and therefore sends replies back through the same physical network adapter from which the request initiated. The vSwitch port-based policy is best used when the number of virtual network adapters is greater than the number of physical network adapters. In the case where there are fewer virtual network adapters than physical adapters, some physical adapters will not be used. For example, if five virtual machines are connected to a vSwitch with six uplinks, only five used vSwitch ports will be assigned to exactly five uplinks, leaving one uplink with no traffic to process.
- Source MAC Load Balancing
- Chapter 5 Installing and Configuring VirtualCenter 2.0
- Multiport match
- Initial loading of extra modules
- Problems loading modules
- 2.2.5. ATM Switching
- 2.6 Драйвер Storport
- Глава 2 Виртуальные машины Virtual PC 2004
- 11.5. Функции getservbyname и getservbyport
- Параметры сокета SO_REUSEADDR и SO_REUSEPORT
- 12.4.2. PortSentry
- Choosing, Configuring, and Installing the Boot Loader




