Книга: Mastering VMware® Infrastructure3
Microsoft Clustering
Разделы на этой странице:
Microsoft Clustering
The network load-balancing (NLB) configuration involves an aggregation of servers that balances the requests for applications or services. In a typical NLB cluster, all nodes are active participants in the cluster and are consistently responding to requests for services. NLB clusters are most commonly deployed as a means of providing enhanced performance and availability. NLB clusters are best suited for scenarios involving Internet Information Services (IIS), virtual private networking, and Internet Security and Acceleration (ISA) Server, to name a few. Figure 10.1 details the architecture of an NLB cluster.
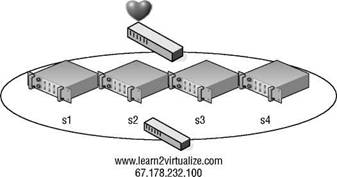
Figure 10.1 An NLB cluster can contain up to 32 active nodes that distribute traffic equally across each node. The NLB software allows the nodes to share a common name and IP address that is referenced by clients.
NLB Support from VMware
As of this writing, VMware does not support the use of NLB clusters across virtual machines. This is not to say it cannot be configured, or that it will not work; however, it is not a VMware-supported configuration.
Unlike NLB clusters, server clusters are used solely for the sake of availability. Server clusters do not provide performance enhancements outside of high availability. In a typical server cluster, multiple nodes are configured to be able to own a service or application resource, but only one node owns the resource at a given time. Server clusters are most often used for applications like Microsoft Exchange, Microsoft SQL Server, and DHCP services, which each share a need for a common datastore. The common datastore houses the information accessible by the node that is online and currently owns the resource, as well as the other possible owners that could assume ownership in the event of failure. Each node requires at least two network connections: one for the production network and one for the cluster service heartbeat between nodes. Figure 10.2 details the structure of a server cluster.
The different versions of Windows Server 2003 offer various levels of support for NLB and server clusters. Table 10.1 outlines the cluster support available in each version of Windows Server 2003.
Windows Clustering Storage Architectures
Server clusters built on Windows Server 2003 can only support up to eight nodes when using a fibre channel-switched fabric. Storage architectures that use SCSI disks as direct attached storage or that use a fibre channel-arbitrated loop result in a maximum of only two nodes in a server cluster. Clustering virtual machines in ESX Server utilizes a simulated SCSI shared storage connection and is therefore limited to only two-node clustering. In addition, the clustered virtual machine solution uses only SCSI-2 reservations, not SCSI-3 reservations, and supports only the SCSI miniport drivers, not the STORPort drivers.
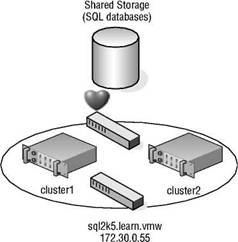
Figure 10.2 Server clusters are best suited for applications and services like SQL Server, Exchange Server, DHCP, etc., that use a common data set.
Table 10.1: Windows Server 2003 Clustering Support
| Operating System | Network Load Balancing (NLB) | Server Cluster |
|---|---|---|
| Windows Server 2003 Web Edition | Yes (up to 32 nodes) | No |
| Windows Server 2003 Standard Edition | Yes (up to 32 nodes) | No |
| Windows Server 2003 Enterprise Edition | Yes (up to 32 nodes) | Yes (up to 8 nodes in fibre channel switch fabric) |
| Windows Server 2003 Datacenter Edition | Yes (up to 32 nodes) | Yes (up to 8 nodes in fibre channel switch fabric) |
MSCS, when constructed properly, provides automatic failover of services and applications hosted across multiple cluster nodes. When multiple nodes are configured as a cluster for a service or application resource, only one node owns the resource at any given time. When the current resource owner experiences failure, causing a loss in the heartbeat between the cluster nodes, another node assumes ownership of the resource to allow continued access with minimal data loss. To configure multiple Windows Server 2003 nodes into a Microsoft cluster, the following requirements must be met:
? Nodes must be running either Windows Server 2003 Enterprise Edition or Datacenter Edition.
? All nodes should have access to the same storage device(s).
? All nodes should have two similarly connected and configured network adapters: one for the production network and one for the heartbeat network.
? All nodes should have Microsoft Cluster Services installed.
- Microsoft Exchange Server
- Clustering Virtual Machines
- Virtual Machine Clustering Scenarios
- Как уменьшить размер документа Microsoft Word?
- Интеграция Windows SharePoint и Microsoft Office
- 3.7 Система Microsoft Exchange 2000 и NAS
- 7.4 Технология виртуализации хранилища от компании Microsoft
- Продукты и технологии Microsoft SharePoint
- Извлечение и возврат документов в приложениях Microsoft Office 2007
- Создание рабочих областей для документов из приложений Microsoft Office 2007
- Часть III Пакет Microsoft Office
- Как в документ Microsoft Word вставить текст, в котором отсутствует форматирование?




