Книга: Fedora™ Unleashed, 2008 edition
The Glade Client for Developing in GNOME
The Glade Client for Developing in GNOME
If you prefer to use GNOME and its development tools, the Glade GTK+ GUI builder can save you time and effort when building a basic skeleton for a program. You launch Glade from the desktop panel's Programming menu.
When you launch Glade, a directory named Projects is created in your home directory, and you see a main window, along with two floating palette and properties windows (see Figure 28.2, which shows a basic GNOME client with a calendar widget added to its main window). You can use Glade's File menu to save the blank project and then start building your client by clicking and adding user interface elements from the Palette window. For example, you can first click the Palette window's Gnome button and then click to create your new client's main window. A window with a menu and a toolbar appears — the basic framework for a new GNOME client!
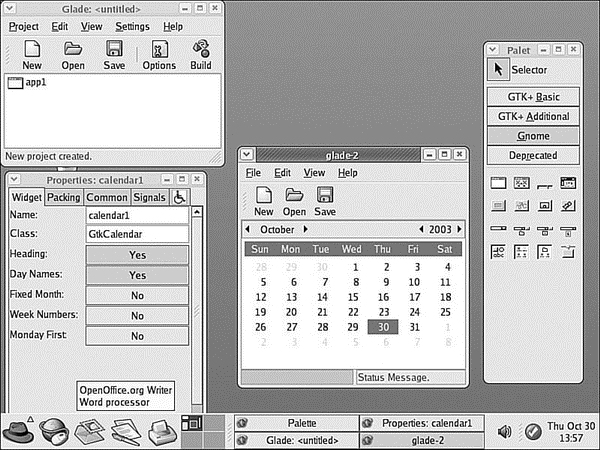
FIGURE 28.2 Glade is 100% backward compatible, which means Glade 2 can read Glade 3 interfaces, and vice versa.
Related Fedora and Linux Commands
You will use many of these commands when programming in C and C++ for Linux:
? ar — The GNU archive development tool
? as — The GNU assembler
? autoconf — The GNU configuration script generator
? cervisia — A KDE client that provides a graphical interface to a CVS project
? cvs — An older project revision control system, now replaced by Subversion
? designer — Trolltech's graphical prototyping tool for use with Qt libraries and X
? gcc — The GNU C/C++ compiler system
? gdb — The GNU interactive debugger
? glade-3 — The GNOME graphical development environment for building GTK+ clients
? gprof — The GNU program profiler
? kdevelop — The KDE C/C++ graphical development environment for building KDE, GNOME, or terminal clients
? make — A GNU project management command
? patch — Larry Wall's source patching utility
? pmake — A BSD project management command
? splint — The C source file checker
? svn — The Subversion version control system
- Forced writes - палка о двух концах
- Forced Writes
- 4.4.4 The Dispatcher
- SERVER CLIENT MAPPING
- About the author
- Chapter 7. The state machine
- Chapter 15. Graphical User Interfaces for Iptables
- Appendix E. Other resources and links
- What NAT is used for and basic terms and expressions
- Example NAT machine in theory
- Information request
- SCTP Generic header format




