Книга: Windows Server 2012 R2 Storage, Security, & Networking Pocket Consultant
Adding address and pointer records
Adding address and pointer records
You use the A and AAAA records to map a host name to an IP address, and the PTR record creates a pointer to the host for reverse lookups. You can create address and pointer records at the same time or separately.
You create a new host entry with address and pointer records by following these steps:
1. In the DNS Manager console, expand the Forward Lookup Zones folder for the server with which you want to work.
2. Press and hold or right-click the domain you want to update, and then tap or click New Host (A Or AAAA). This opens the dialog box shown in Figure 9–6.
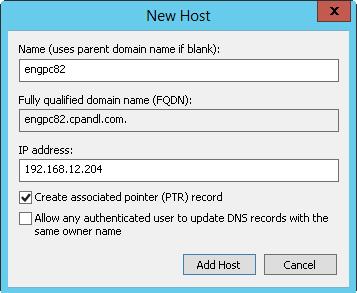
FIGURE 9–6 Create address records and pointer records simultaneously with the New Host dialog box.
3. Enter the single-part computer name, such as servicespc85, and then the IP address, such as 192.168.10.58.
4. Select the Create Associated Pointer (PTR) Record check box.
NOTE You can create PTR records only if the corresponding reverse lookup zone is available. You can create this file by following the steps listed in “Configuring reverse lookups” earlier in this chapter. The Allow Any Authenticated User option is available only when a DNS server is configured on a domain controller.
5. Tap or click Add Host, and then tap or click OK. Repeat these steps as necessary to add other hosts.
6. Tap or click Done when you have finished.
Adding a PTR record later
If you need to add a PTR record later, you can do so by following these steps:
1. In the DNS Manager console, expand the Reverse Lookup Zones folder for the server with which you want to work.
2. Press and hold or right-click the subnet you want to update, and then tap or click New Pointer (PTR).
3. Type the host IP address, such as 192.168.1.95, and then enter the host name, such as servicespc54. Tap or click OK.
- Viewing and updating DNS records
- Разработка приложений баз данных InterBase на Borland Delphi
- Open Source Insight and Discussion
- Introduction to Microprocessors and Microcontrollers
- Chapter 6. Traversing of tables and chains
- Chapter 8. Saving and restoring large rule-sets
- Chapter 11. Iptables targets and jumps
- Chapter 5 Installing and Configuring VirtualCenter 2.0
- Chapter 16. Commercial products based on Linux, iptables and netfilter
- Appendix A. Detailed explanations of special commands
- Appendix B. Common problems and questions
- Appendix E. Other resources and links




