Книга: Windows Server 2012 R2 Storage, Security, & Networking Pocket Consultant
Setting auditing policies
Setting auditing policies
Auditing policies are essential to help ensure the security and integrity of your systems. Just about every computer system on the network should be configured with some type of security logging. You configure auditing policies for individual computers with local Group Policy and for all computers in domains with Active Directory-based Group Policy. Through Group Policy, you can set auditing policies for an entire site, a domain, or an organizational unit. You can also set policies for an individual workstation or server.
After you access the GPO with which you want to work, you can set auditing policies by following these steps:
1. In the Group Policy Management Editor, shown in Figure 4–4, access the Audit Policy node by working your way down the console tree. Expand Computer Configuration, Policies, Windows Settings, Security Settings, and Local Policies, and then select Audit Policy.
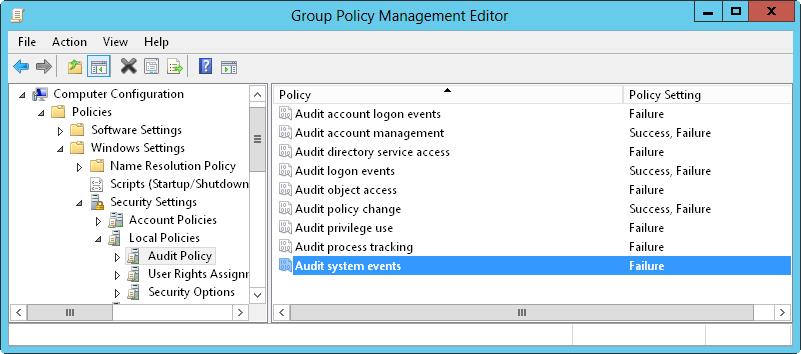
FIGURE 4–4 Set auditing policies by using the Audit Policy node in Group Policy.
2. The auditing options are as follows:
? Audit Account Logon Events Tracks events related to user logon and logoff.
? Audit Account Management Tracks account management by means of Active Directory Users And Computers. Events are generated any time user, computer, or group accounts are created, modified, or deleted.
? Audit Directory Service Access Tracks access to Active Directory. Events are generated any time users or computers access the directory.
? Audit Logon Events Tracks events related to user logon, logoff, and remote connections to network systems.
? Audit Object Access Tracks system resource usage for files, directories, shares, printers, and Active Directory objects.
? Audit Policy Change Tracks changes to user rights, auditing, and trust relationships.
? Audit Privilege Use Tracks the use of user rights and privileges, such as the right to back up files and directories.
NOTE The Audit Privilege Use policy doesn’t track system access-related events, such as the use of the right to log on interactively or the right to access the computer from the network. You track these events with logon and logoff auditing.
? Audit Process Tracking Tracks system processes and the resources they use.
? Audit System Events Tracks system startup, shutdown, and restart, in addition to actions that affect system security or the security log.
3. To configure an auditing policy, double-tap or double-click its entry, or press and hold or right-click the entry, and then tap or click Properties.
4. In the dialog box that is displayed, select the Define These Policy Settings check box, and then select either the Success check box, the Failure check box, or both. Success logs successful events, such as successful logon attempts. Failure logs failed events, such as failed logon attempts.
5. Tap or click OK.
When auditing is enabled, the security event log will reflect the following:
? Event IDs of 560 and 562 detailing user audits
? Event IDs of 592 and 593 detailing process audits
- Auditing files and folders
- Auditing system resources
- Setting up default policies
- Setting up user specified chains in the filter table
- Для чего нужны папки Windows, Documents and Settings, Program Files и Temp?
- После переустановки Windows нет доступа к папке Мои документы или нельзя удалить оставшуюся от старой системы папку Docu...
- CHAPTER 22 Setting Up a Proxy Server
- Setting the Time Zone
- Setting Up an SSH Server
- Editing Printer Settings
- Setting Up a Telnet Server
- Setting Up Guest Operating Systems




