Книга: Fedora™ Unleashed, 2008 edition
Using the Fedora Internet Configuration Wizard
Using the Fedora Internet Configuration Wizard
The Fedora Modem Configuration Wizard can be used to set up the many kinds of network connection types that exist. Fedora provides wizards for the following connections:
? IPSec (VPN) connection (virtual private network using crypto IP encapsulation)
? Ethernet connection
? ISDN connection
? Modem connection
? Token Ring connection
? Wireless connection
? xDSL connection
The example provided here uses the wizard to configure a modem connection — the most commonly encountered home network connection. The other types are configured in essentially the same manner.
From the System menu, select the Administration submenu and click Network to open the Network Configuration tool. Enter the root password to gain access to the tool and click New in the toolbar to start the wizard. Select Modem Connection from the list of options, shown in Figure 14.4, and click Forward.
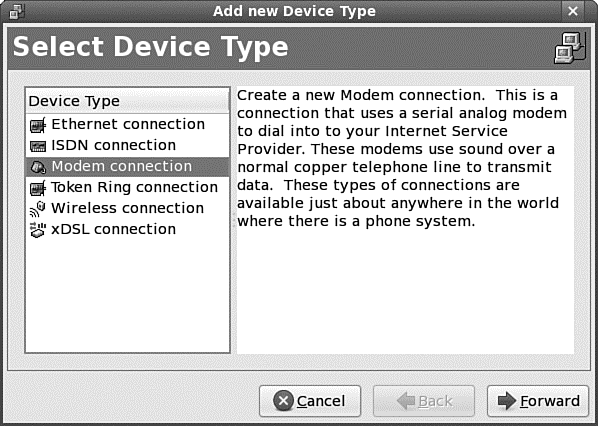
FIGURE 14.4 The Network Configuration tool can be used to quickly and easily configure many different kinds of Internet connections.
Select Modem Connection in the Device Type list, and then click the Forward button. You are then asked to select a provider, designate a name for the service, enter your ISP's phone number, and enter your username and password on the remote system, as shown in Figure 14.5. A dialing prefix (to disable call waiting, for example) can be added in the Prefix field. Additional special settings are also included for PPP users in various countries with different ISPs, as shown by the country flags on the left.
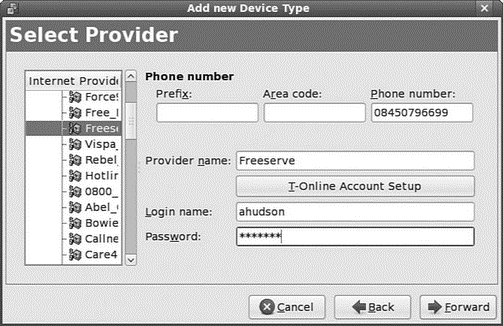
FIGURE 14.5 Enter a name for your ISP's service, along with the telephone number, user- name, and password for the service.
Enter the telephone number of your ISP's remote computer's modem. Enter a country code if needed, along with an area code and telephone number. Note that some areas require a 10-digit number for local telephone service. When finished, click the Forward button. You'll then be asked about IP address settings; unless you have specific instructions from your ISP, you should leave the automatic option enabled. Finally, you are able to confirm the settings. Click the Apply button to create the interface. When you have finished, you will see a new ppp0 entry in the Network Configuration window, as shown in Figure 14.6.
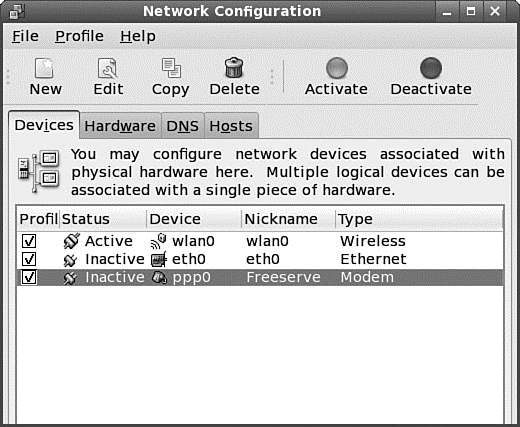
FIGURE 14.6 Your new PPP dialup connection appears in the Network Configuration dialog, which also shows the status of the connection.
To edit the new connection identified as ppp0, select the interface and then click the Edit button. A configuration dialog appears, as shown in Figure 14.7. Each tab presents an easy-to-use interface for setting dialup options.
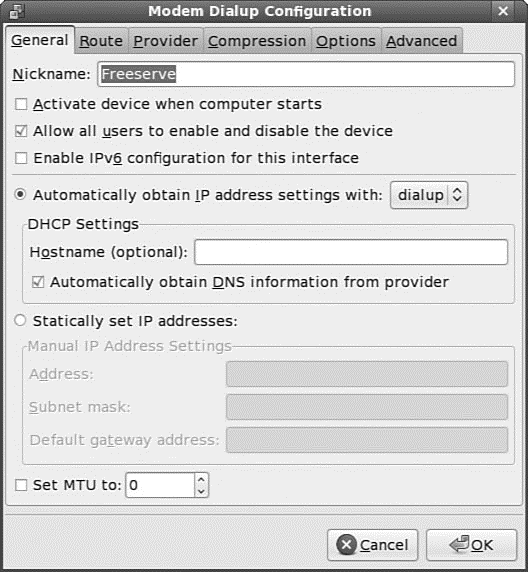
FIGURE 14.7 Here you can edit the dialup configuration, if necessary, to set IP addresses and other custom values; the defaults work for most people.
This window can be reached later from the System Settings menu as the Network menu item. Fedora also provides a simple control interface via the System, Administration menu as the Network Device Control menu item, as shown in Figure 14.8.
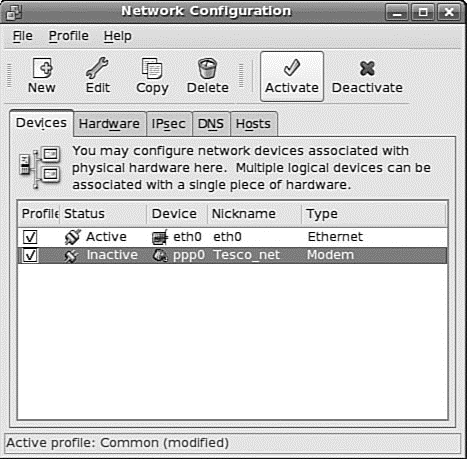
FIGURE 14.8 The Network Device Control enables you to start and stop a network interface.
Launch a PPP connection by selecting the ppp0 interface and then clicking the Activate button.
You can also use the ifup command manually (only as root) to bring up the connection like this:
# ifup ppp0
To close the connection manually, use ifdown:
# /sbin/ifdown ppp0
If you named the dialup connection something other than ppp0, use that name instead. Because this one is named Cavtel, it can be brought up manually with the following:
# ifup Cavtel
- 4.4.4 The Dispatcher
- About the author
- Chapter 7. The state machine
- Appendix E. Other resources and links
- Caveats using NAT
- Example NAT machine in theory
- Using Double Quotes to Resolve Variables in Strings with Embedded Spaces
- The final stage of our NAT machine
- Compiling the user-land applications
- The conntrack entries
- Untracked connections and the raw table
- Basics of the iptables command




