Книга: Fedora™ Unleashed, 2008 edition
Group Management Tools
Group Management Tools
Fedora provides several command-line tools for managing groups as well as graphical tools. Many experienced sysadmins prefer the command-line tools because they are quick and easy to use and they can be included in scripts if the sysadmin desires to script a repetitive task. Here are the most commonly used group management command-line tools:
? groupadd — This command creates and adds a new group.
? groupdel — This command removes an existing group.
? groupmod — This command creates a group name or GIDs, but doesn't add or delete members from a group.
? gpasswd — This command creates a group password. Every group can have a group password and an administrator. Use the -A argument to assign a user as group administrator.
? useradd -G — The -G argument adds a user to a group during the initial user creation. (More arguments are used to create a user.)
? usermod -G — This command enables you to add a user to a group as long as the user is not logged in at the time.
? grpck — A command for checking the /etc/group file for typos.
As an example, imagine that there is a DVD-RW device (/dev/scd0) computer to which the sysadmin wants a regular user named vanessa to have access. To grant vanessa that access, he would use these steps:
1. Add a new group with the groupadd command:
# groupadd dvdrw
2. Change the group ownership of the device to the new group with the chgrp command:
# chgrp dvdrw /dev/scd0
3. Add the approved user to the group with the usermod command:
# usermod -G dvdrw vanessa
4. Make user vanessa the group administrator with the gpasswd command so that she can add new users to the group:
# gpasswd -A vanessa
Now, the user vanessa has permission to use the DVD-RW drive, as would anyone else added to the group by the super user or vanessa because she is now also the group administrator and can add users to the group.
The sysadmin can also use the graphical interface that Fedora provides, as shown in Figure 10.2. It is accessed as the Users and Groups item from the System Settings menu item.
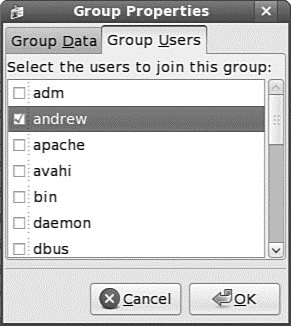
FIGURE 10.2 Just check the box to add a user to a group.
You will note that the full set of group commands and options are not available from the graphical interface, limiting the usefulness of the GUI to a subset of the most frequently used commands. You learn more about using the Fedora User Manager GUI in the next section.
- Managing Groups
- User Management Tools
- Graphical Development Tools
- Logical Volume Management
- 9.3. MEMORY MANAGEMENT IN CHORUS
- 5.2 Hardware Development Tools
- ? Adding Power Management Support
- Process Management API
- Thread Management API
- Power Management API
- IClass Power Management Interfaces
- System tools used for debugging




