Книга: Microsoft Windows Embedded CE 6.0 Exam Preparation Kit
Memory Management Unit
Memory Management Unit
Windows Embedded CE 6.0 requires the processor to provide a memory mapping mechanism to associate physical memory with virtual memory, up to a maximum of 512 MB of mapped physical memory. Figure 5-8 shows an example with 32 MB of flash memory and 64 MB of RAM mapped into the cached and non-cached static mapping regions of the kernel. On ARM-based and x86-based platforms, the memory mapping relies on a user-defined OEMAddressTable, whereas on the SHx-based and MIPS-based platforms, the mapping is directly defined by the CPU. The Memory Management Unit (MMU) is responsible for managing the physical-to-virtual address mappings.
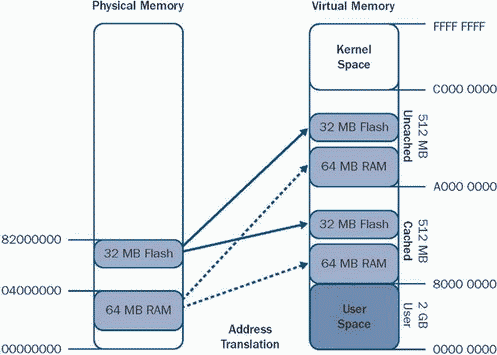
Figure 5-8 Physical-to-virtual memory mapping example
NOTE MMU initialization
The kernel initializes the MMU and creates the necessary page tables during system startup. This processor-specific part of the kernel depends on the architecture of the hardware platform. For implementation details, refer to the Windows Embedded CE private code, located in subdirectories per processor type under %_PRIVATEROOT%WinceosCoreosKernel.
- EVENT MEMORY SIZE
- 9.3.3. Distributed Shared Memory
- Chapter 13: Memory Management
- 13.2 Dynamic Memory Allocation in Embedded Systems
- 13.2.1 Memory Fragmentation and Compaction
- 13.3 Fixed-Size Memory Management in Embedded Systems
- 13.4 Blocking vs. Non-Blocking Memory Functions
- 13.5 Hardware Memory Management Units
- Unit Testing
- System Memory Mapping
- Часть II На примере xUnit
- CHAPTER 17 Apache Web Server Management




