Книга: Mastering VMware® Infrastructure3
Installing a Guest Operating System
Разделы на этой странице:
Installing a Guest Operating System
A new virtual machine is analogous to a physical computer with an empty hard drive. All the components are installed but there is no operating system. Once the virtual machine has been created, a supported guest operating system can be installed. Some of the more commonly installed guest operating systems supported by ESX 3.0 include:
? Windows Vista
? Windows Server 2003 Web/Standard/Enterprise/Datacenter
? Windows Small Business Server 2003
? Windows XP
? Windows 2000
? Windows NT 4
? Red Hat Enterprise Linux 2.1/3.0/4.0
? SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 8/9/10
? NetWare 5.1/6.0/6.5
? Solaris 10 operating system for x86 platforms
Installing any of these supported guest operating systems follows the same common order of steps for installation on the physical server, but the nuances and information provided during the install of each guest operating might vary greatly.
Perform the following steps to install a guest operating system using an ISO file on a shared datastore:
1. Use the VI Client to connect to a VirtualCenter server or an individual ESX Server host where a virtual machine has been created.
2. In the inventory tree, right-click the new virtual machine and select the Edit Settings menu option. The virtual machine properties window will open.
3. Select the CD/DVD Drive 1 hardware option.
4. Select the Datastore ISO File radio button and enable the checkbox Connect At Power On.
5. Click the Browse button to browse a datastore for the ISO file of the guest operating system.
6. Navigate through the available datastore options to find the ISO file of the guest operating system to be installed. Once the ISO file is selected, the properties page will be configured similar to Figure 6.15.
7. Right-click the virtual machine and select the Open Console option. Alternatively, you can use the Console in the details pane of the VI Client application.
8. Click the green Power On button from the toolbar of the console session. Alternatively, you can click the VM menu and select the Power On option. The virtual machine will boot from the mounted CD-ROM ISO file and begin the installation of the guest operating system, as shown in Figure 6.16.
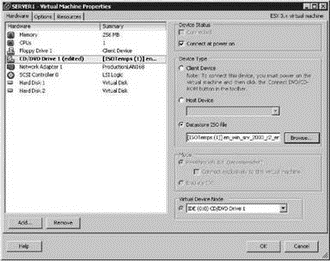
Figure 6.15 A CD-ROM or an ISO file must be configured for the virtual machine to install a guest operating system.
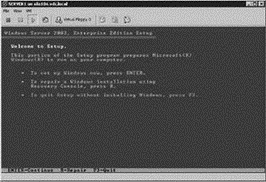
Figure 6.16 When the new virtual machine is turned on for the first time, it will boot from the CD-ROM to begin the installation of the guest operating system.
9. Follow the onscreen instructions to complete the guest operating system installation. After installing the guest operating system, you should then install the VMware Tools. We will discuss the VMware Tools installation and configuration in the next section.
Microsoft Licensing and Windows Activation for Virtual Machines
In the fourth quarter of 2005 Microsoft announced a radical change in the licensing of Windows Server 2003 operating system within a virtual infrastructure. To date, there is still confusion about the virtualization licensing available for the Windows Server 2003 operating system. The following list of licensing data is a culmination of information from both Microsoft and VMware:
? A single licensed copy of Windows Server 2003 R2 Datacenter Edition can be use to install and run an unlimited number of virtual machines on a single physical server. The following image shows the Windows Server 2003 R2 Enterprise and Datacenter Edition licensing schemes:
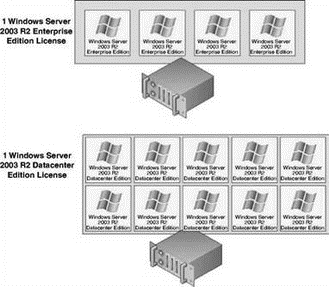
? Windows Server 2003 Web Edition and Windows Server 2003 Standard Edition are not affected by the new licensing terms and must be licensed on a per-virtual machine basis to maintain compliance with the Microsoft Licensing agreement.
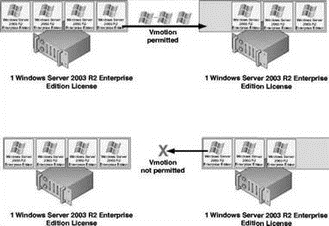
? VMotion, moving a running virtual machine to a new host, does not violate a Microsoft Licens ing agreement as long as the target ESX Server host is licensed for the post-VMotion number of virtual machines. For example, if an ESX Server host named SILO101 has four running virtual machines and a second ESX host named SILO102 has three running virtual machines, it is within the licensing agreement to perform a VMotion of one virtual machine from SILO101 to SILO102. However, a VMotion from SILO102 to SILO101 would violate the licensing agreement. The next image exemplifies this scenario:
? Microsoft applications licensed on a per-processor basis must be licensed per virtual processor. For example, installing SQL Server 2005 in two virtual machines with two virtual processors requires four licenses for SQL Server 2005.
With the new licensing structure in place, using ESX Server with multicore processors and a hefty helping of RAM provides a substantial return on investment.
If your licensing structure for a Windows Server guest operating system does not fall under the umbrella of a volume licensing agreement, you will be required to activate the operating system with Microsoft within 60 days of installation. Activation can be done automatically over the Internet or by calling the provided regional phone number. With Windows Server operating systems specifically, the activation algorithm takes into account the hardware specifications of the server. In light of this, Windows must be reactivated when enough hardware changes have been made to significantly change the operating systems. To facilitate the activation process and especially to reduce the possibility of reactivation, the VMware Tools installation, memory adjustments, and processor adjustments should be made prior to performing the activation.
In addition to installing the VMware Tools, you should perform any necessary tweaks or adjustments to enhance the performance of the virtual machine. For example, in a Windows guest operating system, configuring the hardware acceleration to its maximum setting provides a much smoother console session performance.
Perform the following steps to adjust the hardware acceleration in a Windows guest operating system:
1. Right-click an empty area of the Windows desktop and select the Properties option.
2. Select the Settings tab and click the Advanced button.
3. Select the Troubleshooting tab.
4. As shown in Figure 6.17, move the Hardware Acceleration slider bar to the Full setting on the right.
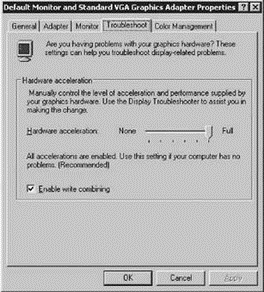
Figure 6.17 Adjusting the hardware acceleration feature of a Windows guest operating system is a common and helpful adjustment for improving mouse performance.
Virtual Machine Guest Operating Systems
For a complete list of guest operating systems and all respective information regarding installation notes and known issues, please refer to the PDF available from the VMware.com website at http://www.vmware.com/pdf/GuestOSguide.pdf.
- CHAPTER 16 Xen
- Chapter 6 Creating and Managing Virtual Machines
- Installing the VMware Tools
- Chapter 6: Creating and Managing Virtual Machines
- Chapter 5 Installing and Configuring VirtualCenter 2.0
- System tools used for debugging
- Integrated Secure Communications System
- Когда включаю компьютер, при загрузке пишется Insert system disk and press enter. Что нужно делать?
- На всех дисках моего компьютера есть папка System Volume Information. Для чего она нужна?
- 14.5.1. Open Systems Interconnection
- 5.3. TRENDS IN DISTRIBUTED FILE SYSTEMS
- Абстрактный базовый класс FileSystemInfo




