Книга: Windows Server 2012 R2 Storage, Security, & Networking Pocket Consultant
Assigning user logon and logoff scripts
Assigning user logon and logoff scripts
You can assign user scripts in one of the three following ways:
You can assign logon and logoff scripts as part of a GPO; and as a result, all users who are members of the site, domain, or organizational unit-or all three-execute scripts automatically when they log on or log off.
You can also assign logon scripts individually through the Active Directory Users And Computers console, which enables you to assign a separate logon script to each user or group.
You can also assign individual logon scripts as scheduled tasks by using the Scheduled Task Wizard.
To assign a logon or logoff script in a GPO, follow these steps:
1. In File Explorer, open the folder containing the script or scripts you want to use.
2. In the GPMC, press and hold or right-click the GPO for the site, domain, or organizational unit with which you want to work, and then tap or click Edit to open the policy editor for the GPO.
3. Double-tap or double-click the Windows Settings folder in the User
ConfigurationPolicies node, and then tap or click Scripts.
4. To work with logon scripts, press and hold or right-click Logon, and then tap or click Properties. To work with logoff scripts, press and hold or right-click Logoff, and then tap or click Properties. This opens a dialog box similar to the one shown in Figure 6–4.
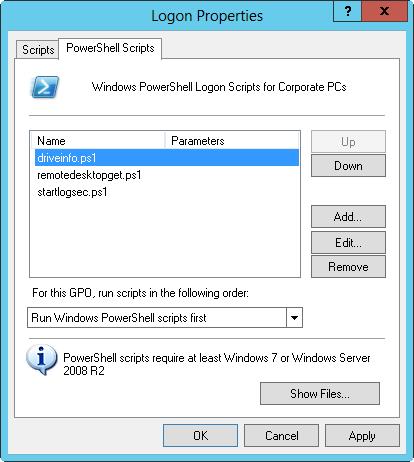
FIGURE 6–4 Add, edit, and remove user logon scripts by using the Logon Properties dialog box.
5. On the Scripts tab, you can manage command-shell batch scripts ending with the.bat or.cmd extension and scripts that use the Windows Script Host. On the PowerShell Scripts tab, you can manage Windows PowerShell scripts. When working with either tab, tap or click Show Files.
6. Copy the files in the open File Explorer window, and then paste them into
the window that opened when you clicked Show Files.
7. Tap or click Add to open the Add A Script dialog box and assign a script. In the Script Name text box, enter the name of the script you copied to the UserScriptsLogon or the UserScriptsLogoff folder for the related policy. In the Script Parameter text box, enter any parameters to pass to the script. Repeat this step to add other scripts.
8. During logon or logoff, scripts are executed in the order in which they’re listed in the Properties dialog box. On the Scripts tab, use the Up and Down buttons to reorder scripts as necessary. Do the same on the PowerShell Scripts tab, on which you can also use the selection list to specify whether Windows PowerShell scripts should run before or after other types of scripts.
9. If you want to edit the script name or parameters later, select the script in the Script For list, and then tap or click Edit. To delete a script, select the script in the Script For list, and then tap or click Remove.
10. To save your changes, tap or click OK.
- Разработка приложений баз данных InterBase на Borland Delphi
- Open Source Insight and Discussion
- Introduction to Microprocessors and Microcontrollers
- Chapter 6. Traversing of tables and chains
- Chapter 8. Saving and restoring large rule-sets
- Chapter 11. Iptables targets and jumps
- Chapter 12. Debugging your scripts
- Chapter 5 Installing and Configuring VirtualCenter 2.0
- Chapter 14. Example scripts
- Chapter 15. Graphical User Interfaces for Iptables
- Chapter 16. Commercial products based on Linux, iptables and netfilter
- Appendix A. Detailed explanations of special commands




