Книга: Fedora™ Unleashed, 2008 edition
Configuring Your Firewall
Configuring Your Firewall
Always use a hardware-based or software-based firewall on computers connected to the Internet. Fedora includes a graphical firewall configuration client named system-config-securitylevel, along with a console-based firewall client named lokkit. Use these tools to implement selective or restrictive policies regarding access to your computer or LAN.
Start the lokkit command from a console or terminal window. You must run this command as root; otherwise, you will see an error message like this:
$ /usr/sbin/lokkit
ERROR - You must be root to run lokkit.
Use the su command to run lokkit like this:
$ su -c "/usr/sbin/lokkit"
After you press Enter, you see a dialog as shown in Figure 30.1. Press the Tab key to navigate to enable or disable firewalling. You can also customize your firewall settings to allow specific protocols access through a port and to designate an ethernet interface for firewalling if multiple NICs are installed. Note that you can also use a graphical interface version of lokkit by running the gnome-lokkit client during an X session.
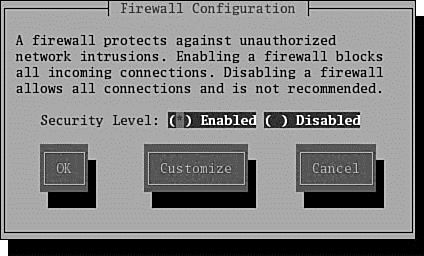
FIGURE 30.1 Fedora's lokkit command quickly generates firewall rules in memory for Linux.
Using system-config-securitylevel is a fast and easy way to implement a simple packet-filtering ruleset with filtering rules used to accept or reject TCP and UDP packets flowing through your host's ethernet or designated device, such as eth0 or ppp0. The rules are created on the fly and implemented immediately in memory with iptables.
Start system-config-securitylevel from the Administration menu's Firewall menu item. You are prompted for the root password and the client's window then appears. Figure 30.2 shows firewalling enabled for the eth0 ethernet device, allowing incoming secure shell and HTTP requests.
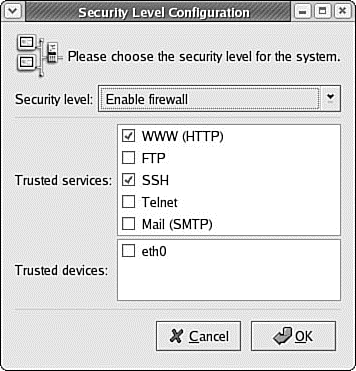
FIGURE 30.2 Fedora's system-config-securitylevel client can also be used to quickly generate and implement standard or simple custom firewall rules for Linux.
You can use Fedora to create a custom firewall, perhaps supporting IP masquerading (also known as NAT) by using either ipchains or iptables. You'll find two sample scripts under the /usr/share/doc/rp-pppoe/configs directory; these are used when a digital subscriber line (DSL) is used for Internet connection.
- Chapter 12. Debugging your scripts
- Configuring DSL Access
- Configuring a PPPoE Connection Manually
- CHAPTER 30 Securing Your Machines
- Configuring the Kernel for IP Accounting
- Chapter 5 Installing and Configuring VirtualCenter 2.0
- Chapter 13. rc.firewall file
- example rc.firewall
- explanation of rc.firewall
- rc.firewall.txt script structure
- rc.firewall.txt
- rc.DMZ.firewall.txt




