Книга: Fedora™ Unleashed, 2008 edition
Using Fedora's BIND Configuration Tool
Using Fedora's BIND Configuration Tool
Fedora provides a dozen or more different graphical configuration tools system administrators can use to configure network (and system) services. One of these tools is system-config-bind, a deceptively simple BIND configuration tool that requires an active X session and must be run with root privileges.
You can launch this client by using the command system-config-bind from a terminal window or by selecting the Domain Name Service menu item from the Server Settings menu. system-config-bind is automatically installed if you select the Fedora configuration tools.
NOTE
Using system-config-bind and then saving any changes overwrites existing settings! If you prefer to manually edit your named configuration files, do not use system-config-bind. Always make a backup of the configuration files in any event — you'll be glad you did.
After you type the root password and press the Enter key, the client launches. You then see its main window, as shown in Figure 23.2.
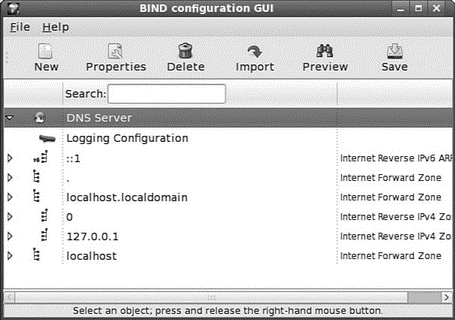
FIGURE 23.2 Fedora's system-config-bind utility can be used to create, modify, and save basic domain nameserver settings.
system-config-bind can be used to add a forward master zone, reverse master zone, MX records, or slave zone. Click the New button to select an entry for configuration, as shown in Figure 23.3.
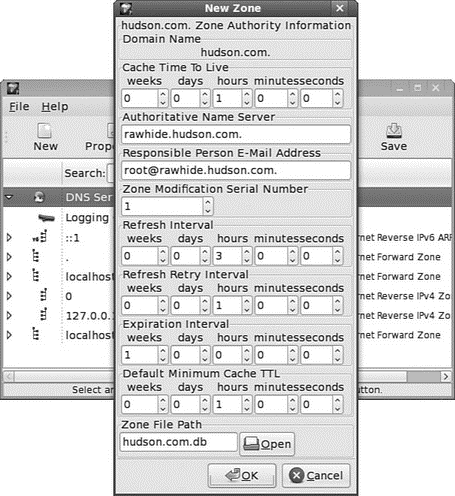
FIGURE 23.3 Use system-config-bind to add a new DNS record to your server or edit the existing settings.
You can edit or delete existing settings by first selecting and then clicking the Properties or Delete button in the system-config-bind dialog. When you finish entering or editing your custom settings, select the Save menu item from the File menu. Configuration files are saved in /etc/named.conf and under the /var/named directory.
- Using Network Configuration Tools
- Using the Network File System
- Providing DNS for a Real Domain with BIND
- Resolver Configuration
- Troubleshooting DNS
- Troubleshooting Problems in Zone Files
- Tools for Troubleshooting
- Caveats using NAT
- Using Double Quotes to Resolve Variables in Strings with Embedded Spaces
- System tools used for debugging
- Other debugging tools




