Книга: Real-Time Concepts for Embedded Systems
15.7.3 Multiple Input Communication Channels
15.7.3 Multiple Input Communication Channels
A daemon task usually has multiple data input sources and multiple event input sources, as shown in Figure 15.19. Consider a daemon task that processes data from an I/O device and has a periodic timer, which is used for recovery if the device is stuck in an inconsistent state. The system timer ISR signals the periodic timer event; this event does not carry data. In such situations, an event register combined with a counting semaphore is a much better alternative than using counting semaphores alone for signaling (see Figure 15.10).
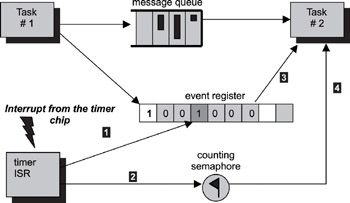
Figure 15.19: Task with multiple input communication channels.
With an event register, each event bit is pre-allocated to a source. In this design pattern, one event bit is assigned to the I/O task #1 and another bit is assigned to the timer ISR. The task blocks on an event register, and an event from either source activates the task. The I/O task first inserts the data associated with an I/O device into the message queue. Then the I/O task signals this event to the task by setting the event's assigned bit in the event register. The timer ISR sets the event bit; this event is no more than a tick announcement to the task. After the task resumes execution, it performs the appropriate action according to the event-register state.
Because the event register is only used as a signaling mechanism, a counting semaphore is used to keep track of the total number of tick occurrences. Listing 15.4 puts this discussion into perspective. The addition of the counting semaphore does not increase the code complexity.
Listing 15.4: Pseudo code for using a counting semaphore for event accumulation combined with an event-register used for event notification.
while (the_events = wait for events from Event-Register)
if (the_events& EVENT_TYPE_DEVICE)
while (Get message from msgQueue)
process the message
endwhile
endif
if (the_events& EVENT_TYPE_TIMER)
counter = 0
disable(interrupts)
while (Get(Counting_Semaphore))
counter = counter + 1
endwhile
enable(interrupts)
if (counter › 1)
recovery time
else
process the timer tick
endif
endif
endwhile
- 15.7.1 Data Transfer with Flow Control
- 15.7.2 Asynchronous Data Reception from Multiple Data Communication Channels
- 15.7.3 Multiple Input Communication Channels
- 15.7.4 Using Condition Variables to Synchronize between Readers and Writers
- 15.7.5 Sending High Priority Data between Tasks
- 15.7.6 Implementing Reader-Writer Locks Using Condition Variables
- 15.7.2 Asynchronous Data Reception from Multiple Data Communication Channels
- INPUT chain
- Integrated Secure Communications System
- The Impossibility of Communication
- Multiple Inheritance
- Searches for a String in Input with grep
- Multiple Terminals
- Multiple Associative Container
- 15.4. Debugging Multiple Tasks
- 15.4.1. Debugging Multiple Processes
- 3.2 PIC Microcontroller Input-Output Port Programming
- 1.3.5 Reset Input




