Книга: Linux Network Administrator Guide, Second Edition
Gateways
Gateways
Subnetting is not only a benefit to the organization; it is frequently a natural consequence of hardware boundaries. The viewpoint of a host on a given physical network, such as an Ethernet, is a very limited one: it can only talk to the host of the network it is on. All other hosts can be accessed only through special-purpose machines called gateways. A gateway is a host that is connected to two or more physical networks simultaneously and is configured to switch packets between them.
Figure 2.2 shows part of the network topology at Groucho Marx University (GMU). Hosts that are on two subnets at the same time are shown with both addresses.
Figure 2.2: A part of the net topology at Groucho Marx University
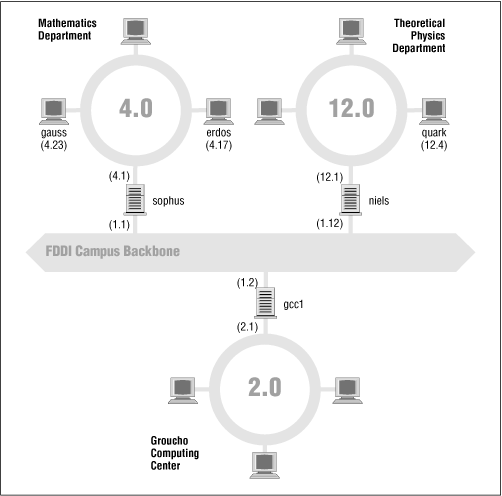
Different physical networks have to belong to different IP networks for IP to be able to recognize if a host is on a local network. For example, the network number 149.76.4.0 is reserved for hosts on the mathematics LAN. When sending a datagram to quark, the network software on erdos immediately sees from the IP address 149.76.12.4 that the destination host is on a different physical network, and therefore can be reached only through a gateway (sophus by default).
sophus itself is connected to two distinct subnets: the Mathematics department and the campus backbone. It accesses each through a different interface, eth0 and fddi0, respectively. Now, what IP address do we assign it? Should we give it one on subnet 149.76.1.0, or on 149.76.4.0?
The answer is: "both." sophus has been assigned the address 149.76.1.1 for use on the 149.76.1.0 network and address 149.76.4.1 for use on the 149.76.4.0 network. A gateway must be assigned one IP address for each network it belongs to. These addresses - along with the corresponding netmask - are tied to the interface through which the subnet is accessed. Thus, the interface and address mapping for sophus would look like this:
| Interface | Address | Netmask |
|---|---|---|
| eth0 | 149.76.4.1 | 255.255.255.0 |
| fddi0 | 149.76.1.1 | 255.255.255.0 |
| lo | 127.0.0.1 | 255.0.0.0 |
The last entry describes the loopback interface lo, which we talked about earlier.
Generally, you can ignore the subtle difference between attaching an address to a host or its interface. For hosts that are on one network only, like erdos, you would generally refer to the host as having this-and-that IP address, although strictly speaking, it's the Ethernet interface that has this IP address. The distinction is really important only when you refer to a gateway.




