Книга: Distributed operating systems
10.6.2. Security Components
10.6.2. Security Components
The DCE security system consists of several servers and programs, the most important of which are shown in Fig. 10-26. The registry server manages the security data base, the registry, which contains the names of all the principals, groups, and organizations. For each principal, it gives account information, groups and organizations the principal belongs to, whether the principal is a client or a server, and other information. The registry also contains policy information per cell, including the length, format, and lifetime for passwords and related information. The registry can be thought of as the successor to the password file in UNIX (/etc/passwd). It can be edited by the system administrator using the registry editor. These can add and delete principals, change keys, and so on.
The authentication server is used when a user logs in or a server is booted. It verifies the claimed identity of the principal and issues a kind of ticket (described below) that allows the principal to do subsequent authentication without having to use the password again. The authentication server is also known as the ticket granting server when it is granting tickets rather than authenticating users, but these two functions reside in the same server.
The privilege server issues documents called PACs (Privilege AttributeCertificates) to authenticated users. PACs are encrypted messages that contain the principal's identity, group membership, and organizational membership in such a way that servers are instantly convinced without need for presenting any additional information. All three of these servers run on the security server machine in the locked room with the mutant dog outside.
The login facility is a program that asks users their names and passwords during the login sequence. It uses the authentication and privilege servers to do its job, which is to get the user logged in and to collect the necessary tickets and PACs for them.
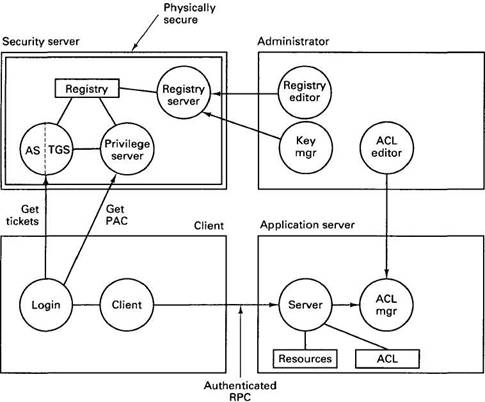
Fig. 10-26. Major components of the DCE security system for a single cell.
Once a user is logged in, he can start a client process that can communicate securely with a server process using authenticated RPC. When an authenticated RPC request comes in, the server uses the PAC to determine the user's identity, and then checks its ACL to see if the requested access is permitted. Each server has its own ACL manager for guarding its own objects. Users can be added or removed from an ACL, permissions granted or removed, and so on, using an ACL editor program.
- 10.1.3. DCE Components
- Installing DHCP components
- Lesson 3: Cloning Components
- Интегрированная безопасность (NT Integrated Security)
- 7.7.2. mod_security
- Managing Password Security for Users
- Managing DNS Security
- UNIX Security Considerations
- DNS Security Considerations
- Using DNS Security Extensions
- Passwords and Physical Security
- Keeping Up-to-Date on Linux Security Issues




