Книга: C# 2008 Programmer
Creating Self- Hosted WCF Service
Разделы на этой странице:
Creating Self- Hosted WCF Service
So far, all the WCF services you have seen are hosted using either a web server or the WCF Service Host. This section shows how you can host a WCF service right from within a Windows Forms application. This example can also be used with the netTCPBinding binding.
The example application is a simple message server that allows clients to send messages to it. Messages received by the service are displayed in a Windows Form.
Creating the WCF Service
Launch Visual Studio 2008 and create a new Windows Forms Application project. Name the project MessageServer.
Populate the default Form1 with a TextBox control, and set its MultiLine property to true (see Figure 20-29).
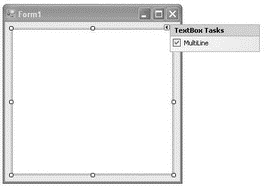
Figure 20-29
Add a new item to the project. Select the WCF Service template, and name it MessageService.cs (see Figure 20-30).
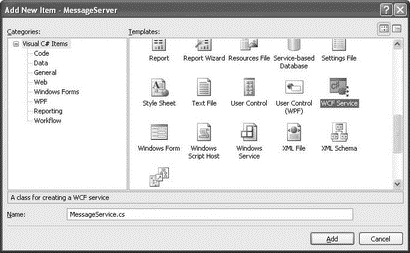
Figure 20-30
In the code-behind of Form1, import the following namespace:
using System.ServiceModel;
Declare the following objects:
public partial class Form1 : Form {
private MessageService service;
private ServiceHost host;
The ServiceHost class is used to host a WCF service. In the Form1_Load event handler, code the following:
private void Form1_Load(object sender, EventArgs e) {
//---host the service---
service = new MessageService(this);
host = new ServiceHost(service);
host.Open();
}
In the design view of Form1, create an event handler for the FormClosing event of Form1 by using the Properties window (see Figure 20-31).
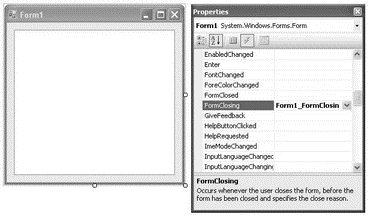
Figure 20-31
Code the Form1_FormClosing event handler as follows:
private void Form1_FormClosing(
object sender, FormClosingEventArgs e) {
//---end the hosting of the service---
host.Close();
}
This code simply ends the hosting of the WCF service when the window is closed.
Define the DisplayMessage() function within the Form1 class as follows:
//---display a message on the TextBox control---
internal void DisplayMessage(string msg) {
textBox1.Text += msg + Environment.NewLine;
}
In the IMessageService.cs file, define the operation contract SetMessage, highlighted here:
namespace MessageServer {
[ServiceContract]
public interface IMessageService {
[OperationContract]
void DoWork();
[OperationContract(IsOneWay = true)]
void SetMessage(string msg);
}
}
The SetMessage() operation uses the one-way messaging pattern because clients simply send messages to the sender and do not need to wait for a response from the server.
This operation allows clients to send a message to the WCF service.
In the MessageService.cs file, add the following highlighted code:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Runtime.Serialization;
using System.ServiceModel;
using System.Text;
namespace MessageServer {
[ServiceBehavior(InstanceContextMode=InstanceContextMode.Single)]
public class MessageService : IMessageService {
private Form1 hostApp;
public void DoWork() {}
//---constructor---
public MessageService(Form1 hostApp) {
//---set which host is hosting this service---
this.hostApp = hostApp;
}
//---called by clients sending a message to the service---
public void SetMessage(string msg) {
//---display the message in Form1---
hostApp.DisplayMessage(msg);
}
}
}
Notice that the MessageService class is prefixed with the [ServiceBehavior] attribute. It contains the InstanceContextMode property, which is set to Single.
Service Behaviors: InstanceContextMode
When a WCF Service receives a message, the message is dispatched to an object's instance methods:
? A single instance of the receiver may be created for all clients, or
? A single instance of the receiver may be created for each client.
The InstanceContextMode property specifies the number of service instances available for handling calls that are contained in incoming messages. It can be one of the following:
? Single — Every received message is dispatched to the same object (a singleton).
? Percall — Every received message is dispatched to a newly created object. This is the default.
? PerSession — Messages received within a session (usually a single sender) are dispatched to the same object.
? Shareable — Messages received within a session (can be one or more senders) are dispatched to the same object.
Edit the App.config file, using the WCF Service Configuration Editor (you can also select it from Tools?WCF Service Configuration Editor).
Set the following details for the first endpoint (see Figure 20-32).
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
Address |
net.tcp://localhost:1234/MessageService |
Binding |
netTcpBinding |
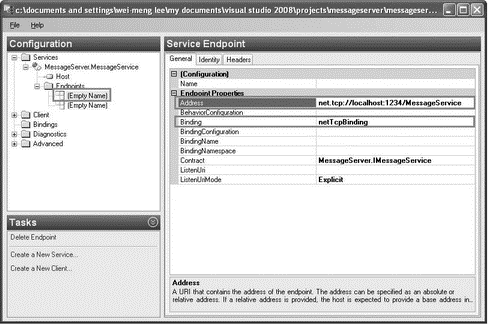
Figure 20-32
Save the file and close the editor.
Basically, you set the endpoint to use the netTcpbinding binding. Examine the App.config file now, and you'll see that the following highlighted code has been added:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<configuration>
...
<services>
<service
behaviorConfiguration="MessageServer.MessageServiceBehavior"
name="MessageServer.MessageService">
<endpoint
address="net.tcp://localhost:l234/MessageService"
binding="netTcpBinding" bindingConfiguration=""
contract="MessageServer.IMessageService">
<identity>
<dns value="localhost"/>
</identity>
</endpoint>
<endpoint address="mex" binding="mexHttpBinding"
contract="IMetadataExchange"/>
<host>
<baseAddresses>
<add
baseAddress="http://localhost:8731/Design_Time_Addresses/MessageServer/MessageService/"/>
</baseAddresses>
</host>
</service>
</services>
</system.serviceModel>
</configuration>
Notice the base address contained in the app.config file:
http://localhost:8731/Design_Time_Addresses/MessageServer/MessageService/
This is the address that clients can use to add a service reference to your WCF service.
Press F5 to test the application now. When prompted with the Windows Security Alert dialog, click Unblock (see Figure 20-33).
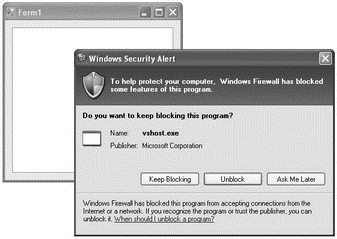
Figure 20-33
In this example, the WCF service is hosted by the Windows Form application, at port 1234, using the TCP protocol.
Creating the Client
Launch another instance of Visual Studio 2008, and create a new Windows Forms Application project. Name it MessageClient.
Populate the default Form1 with the controls shown in Figure 20-34.
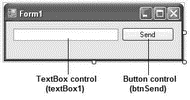
Figure 20-34
Add a service reference to the WCF service created earlier (see Figure 20-35). Enter the base address URL (http://localhost:8731/Design_Time_Addresses/MessageServer/MessageService) that you have observed in the app.config file.
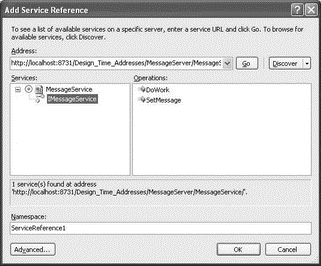
Figure 20-35
Switch to the code-behind of Form1, and import the following namespace:
using System.ServiceModel;
Declare the following member variable:
public partial class Form1 : Form {
ServiceReferencel.MessageServiceClient client;
Double-click the Send button, and code the button1_Click event handler as follows:
private void btnSend_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) {
client = new
MessageClient.ServiceReference1.MessageServiceClient();
client.SetMessage(textBox1.Text);
client.Close();
}
That's it! Press F5 and you can now send a message to the server using the WCF service (see Figure 20-36).
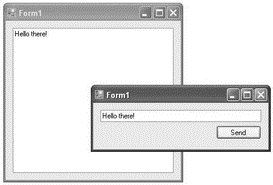
Figure 20-36
- Internet Service Providers who use assigned IP addresses
- Creating CDs from the Command Line
- Получение помощи по Windows SharePoint Services 3.0
- Чтобы установить Service Pack 2, надо ли предварительно устанавливать Service Pack 1?
- Я установил Service Pack 2 для Windows XP, но с ним не хотят работать некоторые программы. Как его удалить из системы?
- Можно ли интегрировать в пакет установки Windows Service Pack и другие обновления, чтобы потом не приходилось их устанав...
- Система просит вставить диск Windows XP и Windows XP Service Pack 2 CD. Но ведь диск с дистрибутивом Windows у меня один...
- 1.1.6. Denial of Service
- Distributed Denial of Service
- Creating and Deleting Device Objects
- Creating a Delegate
- Phone Services




